|
|
| |
| |
Mobile Operating Theatres,
a Cost Effective Way to Transfer
Medical Technologies to Patents
A JOHNSON MEDICAL BULLETIN (2002)
by Agne Nilsson
1.0 Abstract
Mobile operating theatre is a concept of having a fully equipped and fully functional operating theatre, which can be transported from one place to another with ease. The mobile operating theatre is a containerised solution specifically designed for disaster relief. It can also offer immediate or temporary extension to existing medical facility. In the UK, the Government has pledged to reduce long waiting lists and this has led to many healthcare facilities management to opt for this cost effective containerised solution. This is not a rare occurrence in many other developing and developed countries. This bulletin describes the Johnson Medical Mobile Operating Theatre in providing optimal combination of high performance, functionality and mobility.
2.0 Introduction
The mobile operating theatre has full internal facilities to operate on its own. These include all electrical services, mechanical services such as operating theatre ventilation system to provide clean air, medical gas system, plumbing, operating table, operating light, surgical pendants and so forth. These independent mobile operating theatres can therefore be transported to virtually any crisis-ridden locations around the globe.
Due to its modular and integrated design, the Johnson Medical Mobile Operating Theatre has a very short assembly process before it is fully functional, autonomous and ready for operation under clean air condition.
3.0 Basic Construction of Johnson Medical Mobile Operating Theatres
The exterior of the Johnson Medical Mobile Operating Theatre is constructed of steel casing with corrugated steel plates. Standard size cabins can be docked to one another with special locking system to form the entire operating theatre complex complete with preparation room, induction room, scrub area and sterile store.
The containers are of lightweight and watertight construction, and have sufficient strength to maintain the integrity during deployment, use and transportation. The floors, walls and roof panels of the container utilise structural polystyrene or foam core for the temperature and sound insulating properties. Additionally, the roof is properly insulated internally with similar material and finished with aluminium foil paper to further reduce the surface skin heating effects under high solar load conditions. The containers are fitted with appropriate access doors suitable for the function of the container.
Johnson Medical Mobile Operating Theatres ensure that corrosion does not occur on products by careful selection of materials, jointing and finishing processes together with design methods and techniques to ensure that corrosion traps do not occur. The proven techniques and controls are implemented to provide high specification products with an appropriate life and product durability.
The Johnson Medical Mobile Operating Theatres are equipped with virtually all Johnson Medical products. The Johnson Medical Guided AirflowTM Ventilation System is installed in the mobile operating theatre to provide ultra clean air during surgery. The Johnson Medical Guided AirflowTM Ventilation System operates based on the principle that supply air is directed diagonally towards the operating table on the clean side of the room and exhausted out on the uncontrolled air of the room. This ventilation system includes the provision of two large supply air surfaces through which large quantities of sterile/fresh air feed into the co-ejection of the diagonal guided air jet in a controlled and stable manner. This system was developed in Sweden at the end of the eighties and has undergone thorough full-scale testing at the Royal Institute of Technology (KTH) and Royal Public Work Department. Full-scale clinical trials have also been conducted at the Swedish General Hospital, Ryhov Hospital, Jönköping with staff, equipment as well as various operating theatre arrangements. Unique double-wall ventilation exhaust system has been designed to reduce turbulence and to enhance the cooling effect within the operating theatre in hot climates.
The patented ceiling fixture has been designed for the mounting of Johnson Medical’s Aneasthetic Equipment (Dry) & Fluid (Wet) Pendants and Surgeon Pendant. It caters for all other suspended medical equipment in the operating theatre including surgical lights and microscopes, with add-on mountings to allow expansion of surgical techniques.
The majority of the mobile operating theatre interior finishing is covered with high pressure laminated (HPL) boards. These HPL boards are scratch-resistant, anti-bacterial, anti-rust and anti-impact etc. Triple-glazed one-way window has been used to allow filtered natural light in the operating theatre to reduce the feeling of claustrophobia or work-stress after long hours. These windows are designed with a vacuum gap to eliminate moisture and condensation in tropical climate.
High-density laminated doors integrated with a special hydraulic locking system is incorporated into the mobile operating theatre to ensure proper door closing. The Elbow Switch Electric Door is also available as an alternative solution.
The operating theatre is laid with vinyl flooring. There is an 100 mm skirting being laid all around the edges in the operating theatre to provide ease of cleaning and to reduce risks of gathering dusts at sharp edges/corners.
Integrated lighting system is installed in the operating theatre. This lighting system incorporates a special light reflection design capable of producing more than 800 LUX throughout the whole operating theatre. Every single light tube is protected with an acrylic cover for the ease of cleaning and safety.
4.0 Basic Plan Layout of the Johnson Medical Mobile Operating Theatres
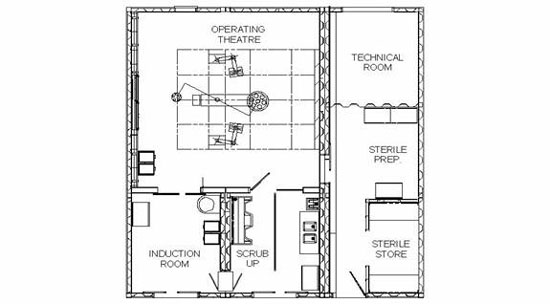 Figure 1: Basic Plan Layout of the Johnson Medical Mobile Operating Theatres
Figure 1: Basic Plan Layout of the Johnson Medical Mobile Operating Theatres
Figure 1 depicts the basic plan layout for Johnson Medical Mobile Operating Theatre Complex, which includes induction room, sterile preparation room, sterile store, scrub-up area and the OT itself. It is also fully equipped with surgical pendants, operating lights, operating table and most importantly the uniquely designed Johnson Medical Guided AirflowTM Ventilation System.
The OT has a standard 6m(W) x 6m(D) x 3m(H) overall dimensions. The rooms are arranged in such a way that it complies with the HTM 2025 medical healthcare facilities requirements. Positive pressure is always maintained in the OT with respect to adjacent rooms. In the case when the sterile preparation room is used as instrument lay-up area, then this area will be at a higher pressure with respect to the OT. This requirement is clearly outlined in HTM 2025.
A technical room has also been incorporated in the entire mobile operating theatre complex. This technical room can also be considered as plant room because most of the mechanical and electrical equipment are positioned in this room. For noise concern, this plant room is fully insulated with higher density insulating material, both to avoid condensation and also to reduce noise level. For the case of structure-borne vibrations, which give rise to noise, all rotating or constantly rattling mechanical components/equipment are mounted on resilient element. This is to induce decaying effects on any vibratory amplitude.
The exterior of the mobile operating theatre is made of steel frames and corrugated steel plates. All exposed surfaces are insulated with insulating material. These corrugated steel plates are said to give better strength, stiffness and structural integrity as compared to the flat sheet metal plates.
Johnson Medical offers turnkey solution to serve the needs of various hospitals and healthcare facilities. As such, the Johnson Medical Mobile Operating Theatre solution includes the consultation on planning, design and the construction of the entire operating theatre complex complete with integrated medical equipment and healthcare facilities, in which is able to cater for customers’ unique needs on mechanical and electrical (M&E) services such as air-conditioning and mechanical ventilation systems, medical gas system, plumbing & sanitary etc. All design and planning is adhering to stringent requirements for operating theatres as governed by the renowned standards such as the HTM 2025, HTM 2022 and ASHRAE.
The minimum requirement for fresh air to the Johnson Medical Mobile Operating Theatre is at a rate of 2,000 m3/hr and exhausted out at a rate of approximately 1,800 m3/hr. This ensures appropriate air change rates throughout the operating theatre and a positive pressure with respect to adjacent rooms is always maintained in the operating theatre.
5.0 Some of the Many Applications and Usage of the Johnson Medical Mobile Operating Theatre
Due to its independency and functionality, the Johnson Medical Mobile Operating Theatre can be used in virtually any situation and anywhere in the world. The most common type of mobile OT cabins is designed for use in field hospitals. These cabins are primarily intended for war or disaster use, such as earthquakes. For this purpose, a very high degree of mobility is required, and the cabin must always be integrated with other units of a field hospital.
The second type of mobile OT cabins are pre-fabricated and primarily used as permanent or semi-permanent extensions of existing hospitals. These cabins can be dismounted and transported to another location. However, as they must comply with normal hospital requirements, these mobile units are usually not locked into the international ISO container standard. Instead they are manufactured considerably larger than the ISO standard size, thus severely limiting their transportability. The containers are often 40-60 ft long and 15-18 ft wide. These dimensions would impose considerable restrictions on mobility in many countries, e.g. through expressway tolls, under bridges and within narrow hospital grounds.
The Johnson Medical Mobile Operating Theatre combines the benefits of high mobility with a fully functional, standard size OT. It complies fully with normal hospital requirements, and also follows the ISO container standard in terms of external size (30 ft long and 10 ft wide). This facilitates transportation by using normal low-bed trucks or low-loader and a standard crane.
Due to limited healthcare facilities in many countries, Governments have pledged to reduce long hospital waiting lists by looking into alternative solutions. This has led to the management of many healthcare facilities to opt for the aforementioned cost effective containerised solution. The Johnson Medical Mobile Operating Theatre is not just an economical solution to ameliorate critical situations, it is also a ‘fast’ solution. The Johnson Medical Mobile Operating Theatre only takes a few hours to build on site. This does not only include the structural works, but also all internal services and fittings before it is fully operational and functional.
Due to geographical complications, it is often impractical and uneconomical to construct hospitals in many remote locations. Needless to say, the mobile operating theatre is of great use in this application.
Mobile operating theatres are also commonly used for disaster relief and military purposes. For economical reasons, there are more and more mobile operating theatres being built to cater to hospital’s “economical” building extensions. In some occasions, these building extensions may even become permanent or part of the existing building. The applications and usage of the Johnson Medical Mobile Operating Theatre are limitless and the above list goes on.
Bibliography & References
- A. Nilsson. Ventilation Systems in Operating Theatres, Aspects to Consider. A Johnson Medical Technical Bulletin, republished 2002.
- A. Nilsson. A Brief Note on the Energy Consumption for Operating Theatre Ventilation System. A Johnson Medical Technical Bulletin, 2002.
Agne Nilsson, Biomed. Eng., MTF, SFAI – Hospital and Research Engineer, Inventor
Agne Nilsson, originally from Sweden, is the Technical Director for Johnson Medical Technology (JMT). He is the founding member of the Swedish Society of Biomedical Engineering and Medical Physics. He also holds membership for the Scandinavian Society of Anaestesiologists and Swedish Society of Inventors. He is the author of the book ‘Medical Equipment Planning’.
Agne Nilsson works on hospital-related projects and has invented and designed a number of systems and medical equipment over the past 30 years. He was awarded the 1986 Development Stipendium by the National Development Foundation. He has extensive international experience on hospital planning. For the past 5 years, he has been working on providing functional and conceptual designs for different government and private projects and departments of hospitals in Malaysia.
|
|
|

